Research Groups at the Physics Department
Applied Quantum Field Theory
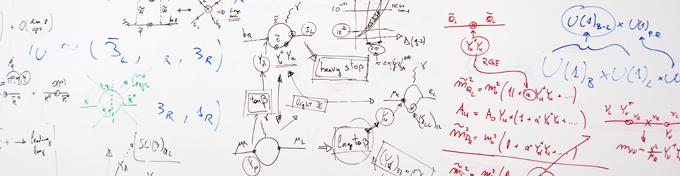
Our group focuses on the development and application of theoretical methods in the physics of strong interactions, the fundamental forces which are responsible for the inner structure of protons and neutrons as well as for the structure of nuclei. The basis of these investigations is Quantum Chromo Dynamics (QCD), the theory of the interaction of quarks and gluons. Part of this program is the investigation of the substructure of baryons and mesons as well as the explanation of the wealth of phenomena resulting from the collective interplay of these particles in nuclei.
Observational Cosmology (Prof. Sherry Suyu)

Through spectacular gravitational lensing effects, our group is shedding light on the dark cosmos: dark energy, dark matter and supermassive black holes.
Biomedical Physics (Prof. Franz Pfeiffer)
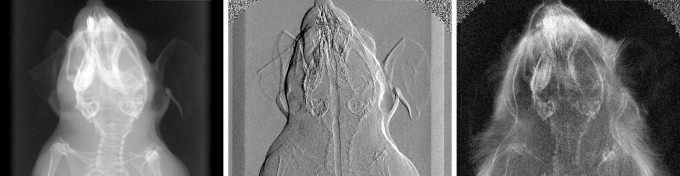
Our interdisciplinary research portfolio is focused on the translation of modern x-ray physics concepts to biomedical sciences and clinical applications. We are particularly interested in advancing conceptually new approaches for biomedical x-ray imaging and therapy. From a medical perspective, our work currently targets early cancer and osteoporosis diagnostics.
Biomolecular Nano-Technology (Prof. Hendrik Dietz)

We develop novel scientific devices and methods for applications in biomolecular physics, biological chemistry, and molecular medicine. To this end, we currently focus on using DNA as a programmable construction material for building nanometer-scale scientific devices with atomically precise features. We also customize proteins and create and study hybrid DNA-protein complexes. 3D transmission electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, and single molecule methods such as optical trapping and fluorescence microscopy are among our routine analysis tools.
Chemical Physics Beyond Equilibrium (Prof. Katharina Krischer)
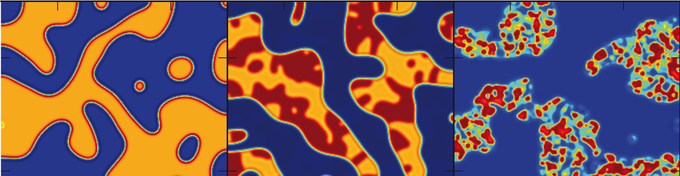
We are working on topics falling into two different areas: Nonlinear Dynamics (e.g. Pattern Recognition, Pattern Formation during Si-Electrodissolution, Pattern Formation in Electrocatalytic Reactions, Complex Ginzburg-Landau Equation) and Artificial Photosynthesis - Photoelectrochemistry.
Dense and Strange Hadronic Matter (Prof. Laura Fabbietti)

We experimentally investigate the properties of strange particles produced in heavy-ion and elementary reactions at intermediate beam energies. Our goal is to understand the interaction of particles which contain a strange quark with nucleons under different density and temperature conditions.
Dark Matter (Prof. Susanne Mertens)

We study the elusive particle, the neutrino, to unlock fundamental mysteries of physics: What is our universe made of? How did structures evolve? Why is our world made of matter and not anti-matter?
Experimental Physics of Functional Spin Systems (Prof. Christian Back)
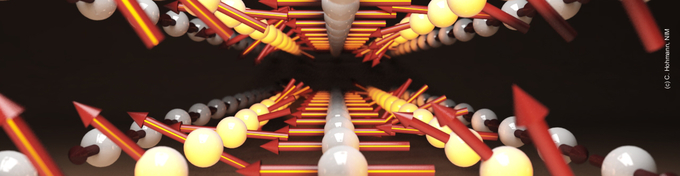
The research of our group is focused on the detailed understanding of magnetization dynamics in hybrid materials comprising of ultrathin magnetic layers in combination with topological materials or with materials inducing strong interfacial spin-orbit interaction. We tailor novel hybrid magnetic structures and investigate their static and dynamic magnetic properties. Among the subjects covered in our research are the dynamics in confined magnetic systems, magnonics, spin orbitronics, hybrid topological materials, high resolution magnetic microscopy as well as magnetic phase transitions in low dimensional systems. In our group we use several techniques to examine magnetization dynamics, the propagation of spinwaves and the efficiency of charge to spin current conversion. At the heart of our research projects are various time and spatially resolved high resolution magnetic microscopy techniques.
Experimental Physics with Cosmic Particles (Prof. Elisa Resconi)

In our group, astro- and particle physics, ground- and space-based experiments, photon and neutrino observations are combined in a scientific program in order to address the following questions: How do astrophysical accelerators work? Do neutrinos have non standard properties, beyond standard oscillation? What is the mass hierarchy of neutrinos? Is the proton stable? Where and what is dark matter?
Experimental Astro-Particle Physics (Prof. Lothar Oberauer)

Neutrino physics with JUNO (Jiangmen Underground Neutrino Observatory). Neutrino oscillation effects, astroparticle physics and search for proton decay.
Experimental Astro-Particle Physics (Prof. Stefan Schönert)

Our group is involved in a number of research projects in neutrino physics and dark matter research.
Experimental Semiconductor Physics (Prof. Martin Stutzmann)

Our work at the Walter Schottky Institut deals with various aspects of new and non conventional semiconductor materials and material combinations: semiconductors with a wide bandgap, disordered semiconductors, advanced thin film systems etc.
Functional Materials (Prof. Peter Müller-Buschbaum)
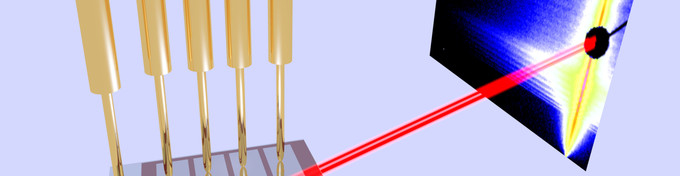
We examine the physical fundamentals of material properties using scattering methods (neutrons-, x-ray and dynamic light scattering). The general goal of our research is to judge from the knowledge of the microscopic dynamics and structure for explaining the functional characteristics of condensed matter.
Hadronic Structure and Fundamental Symmetries (Prof. Stephan Paul)
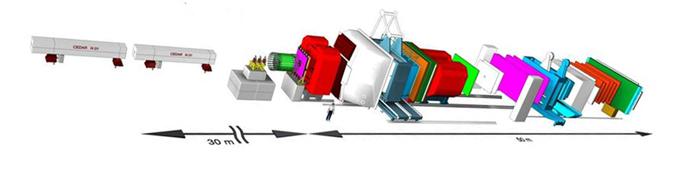
Our group involved in a number of research projects dealing with high energy particle physics and neutron physics.
Semiconductor Nanostructures and Quantum Systems (Prof. Jonathan Finley)

Our group explores a wide range of topics related to the fundamental physics of nanostructured materials and their quantum-electronic and -photonic properties. We study the unique electronic, photonic and quantum properties of materials patterned over nanometer lengthscales and explore how sub-components can be integrated together to realise entirely new materials with emergent properties. This convergence of materials-nanotechnology, quantum electronics and photonics is strongly interdisciplinary, spanning topics across physics, materials science and engineering.
Collective Quantum Dynamics (Prof. Michael Knap)
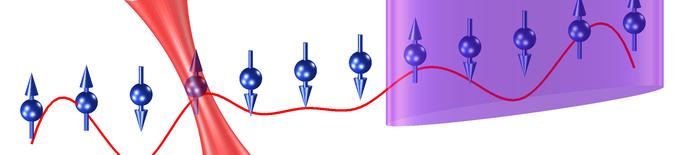
The research of our group aims at a broad range of questions from condensed matter theory and bridges to quantum optics, atomic physics, and computational sciences. Interactions and correlations in condensed matter systems often manifest in striking and novel properties. These properties emerge from collective behavior of the quantum particles. Many examples can be found in nature, including superconductors, quantum magnets and superfluids. Our research address various questions in non-equilibrium quantum dynamics and transport in ultracold quantum gases, interacting light-matter systems, and correlated quantum materials.
Laser and X-Ray Physics (Prof. Reinhard Kienberger)
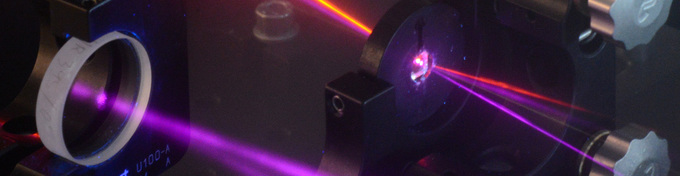
Our group aims at investigating processes inside atoms and molecules on the shortest timescale reached so far, the attosecond timescale. One attosecond compares to one second like one second to the age of the universe. New insight into ever smaller microscopic units of matter as well as in ever faster evolving chemical, physical or atomic processes pushes the frontiers in many fields in science. The interest in these ultrashort processes is the driving force behind the development of sources and measurement techniques that allow time-resolved studies at ever shorter timescales.
Molecular Dynamics (Prof. Martin Zacharias)
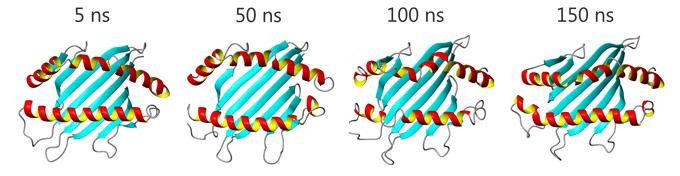
The function of proteins and nucleic acids in living systems is strongly coupled to the molecular motion and dynamics of these biomolecules. Our group uses computer simulation methods to study the structure, function and dynamics of biomolecules. Our goal is to better understand structure formation processes and to elucidate the mechanism of ligand-receptor association in atomic detail.
Molecular Biophysics (Prof. Matthias Rief)
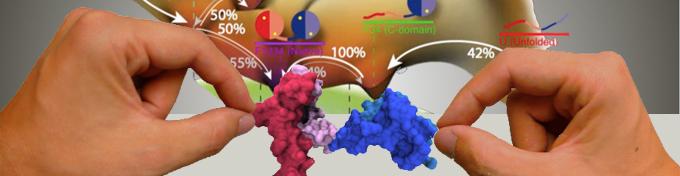
Proteins are fascinating examples of self-organized molecular machines. Without any help a polypeptide strand can fold into functional threedimensional structures. We are interested in studying the function and folding process of proteins on the single molecule level. Examples are single molecule folding/unfolding studies or the motility of molecular motors in optical traps.
Molecular Engineering at Functional Interfaces (Prof. Wilhelm Auwärter)
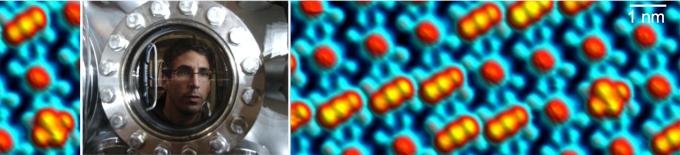
Our research focuses on the creation of nanoscale model systems on atomically tailored surfaces, enabling the study and control of single-molecule processes as well as the self-assembly of supramolecular structures. The studies are inspired by the chemistry of life – which shows how functionally versatile a single set of molecular building blocks can be – and oriented toward innovation in nanotechnology.
Nanotechnology and Nanomaterials (Prof. Alexander Holleitner)
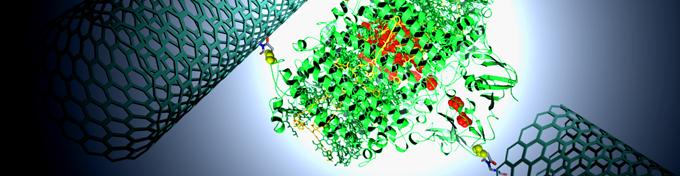
The Holleitner group investigates optoelectronic phenomena in nanoscale circuits with special focus on ultrafast optoelectronics, quantum optoelectronics, and excitonic systems. The research topics aim to fully exploit the potential of nanoscale circuits for optoelectronic and photovoltaic applications, as well as for communication and information technologies.
Neutron Scattering

Scientific activities covered by our group include the fundamental properties of magnetic and superconducting materials (bulk compounds and thin films), materials science and a few selected problems in particle physics. Our group has a long tradition in neutron related research, notably the development of state-of-the-art neutron scattering techniques.
Nuclear Astrophysics

Our group works on a number of research projects on nuclear astrophysics, chemical evolution of the universe, as well as synthesis of nuclear physics, astronomy and stellar theory.
Physics of Surfaces and Interfaces (Prof. Johannes Barth)
Research at E20 aims at the fundamental understanding of interface phenomena and their control for the design of functional nanoarchitectures in reduced dimensions. We investigate and manipulate individual nano-objects and highly organized supramolecular systems.
Physics of Biomedical Imaging (Prof. Julia Herzen)
We develop novel X-ray imaging methods using highly brilliant synchrotron radiation and conventional laboratory X-ray sources. We mainly focus on quantitative multi-modal approaches combining spectral and phase-contrast imaging. Currently, we are aiming at applying these methods for improved breast cancer detection and for quantitative 3D virtual histology of human tissue.
Physics of Energy Conversion and Storage (Prof. Aliaksandr Bandarenka)
We conduct research in the area of the physics of energy conversion and storage. The main topics include the design and implementation of functional materials and a better understanding and characterization of electrified interfaces. The material design is based on a bottom-up approach using input from electrochemical surface science and starting from model surfaces.
Soft Matter Physics (Prof. Christine Papadakis)
The Soft Matter Physics Group investigates the structure, dynamics and kinetics of nanostructured polymer systems, e.g. amphiphilic and switchable block copolymers, thin polymer films, as well as polymers for medical applications. We mainly use scattering methods both at large facilities and in the lab.
Physics of Synthetic Biological Systems (Prof. Friedrich Simmel)

Our goal is the realization of self-organizing molecular systems that are able to respond to their environment, compute, move, take action.
Plasma Surface and Divertor Physics (Prof. Ulrich Stroth)

We represent at the TUM the wide field of plasma physics in research and teaching. The focus of our work lies on magnetized high-temperature plasmas as they exist in fusion experiments as well as in the universe. Of special interest for our research are processes relevant for developing a future energy source based on fusion reactions in magnetically confined plasmas.
Precision Measurements at Extreme Conditions (Prof. Peter Fierlinger)

Our research deals with experiments that should help to understand properties of the early Universe. We currently focus on the nature of the excess of matter versus antimatter. In most scenarios that describe this so-called baryogenesis, new sources of broken symmetries in the early Universe are required. Electric dipole moments (EDM) of fundamental quantum systems are interesting systems to investigate such new sources of CP (or T) violation in the baryon-sector, beyond the Standard Model of particle physics (SM).
Quantum Matter
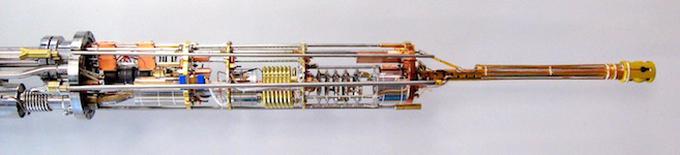
Our group focuses on Quantum Matter, materials with unusual electronic properties. We study these materials by experimental investigations at very low temperature and under high magnetic field and high pressure. Particularly, we are trying to understand the electronic behavior in novel states of matter through a direct detection of the Fermi surface via quantum oscillations, a fundamental “fingerprint” of a material.
Quantum Networks (Prof. Andreas Reiserer)
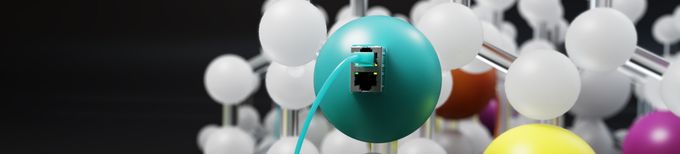
The Quantum Networks Group develops novel hardware for distributed quantum information processing. In particular, erbium dopants in nanophotonic silicon chips are used to generate entanglement between remote quantum systems. The goal of this research is to develop a Quantum Internet in which quantum computers and quantum sensors can be safely connected.
Quantum Technologies (Prof. Menno Poot)
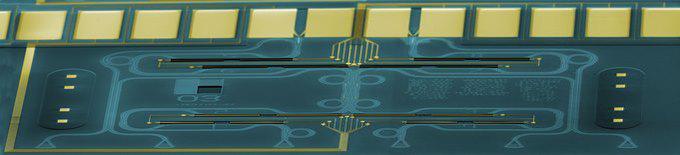
Our group focusses on Quantum Technologies. We make chips using state-of-the-art nanofabrication techniques to study quantum effects in a variety of systems. Another important topic is integrated quantum optics, where photonic chips with functionality to generate, manipulate, and detect single photons are designed, made, and measured.
Technical Physics (Prof. Rudolf Gross, Prof. Stefan Filipp)

The research activities of the Walther-Meißner-Institute are focused on low temperature solid-state and condensed matter physics. The research program is devoted to both fundamental and applied research and also addresses materials science, thin film and nanotechnology aspects.
Theoretical Biophysics of Neuronal Information Processing
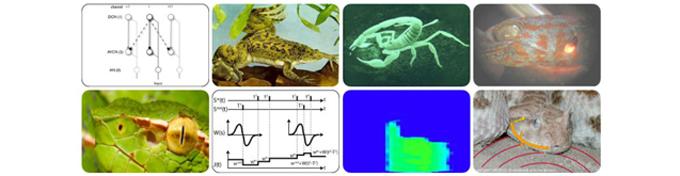
Our basic research goal is to understand the basic units of information processing in the brain. In order to explore the underlying universal principles we focus on sensory systems in the animal world. We search for systems that are on the one hand simple enough to allow a thorough understanding of the system, but on the other hand complex enough to show interesting behavior. In this way, we try to identify fundamental processes that underlying information processing in the brain. Experimental verifiability always plays an important role in our research and we prefer to work together with experimentalists to get an optimal understanding of the problems we are dealing with.
Theoretical Elementary Particle Physics (Prof. Alejandro Ibarra)
The Standard Model of Particle Physics provides an excellent description of nature at distances larger than E-16 cm, or equivalently energies smaller than 100 GeV. However, there are reasons to believe that the Standard Model is incomplete and needs to be extended. Our research group considers extensions of the Standard Model that might account for these observations and we study their consequences for present and future experiments.
Theoretical Elementary Particle Physics (Prof. Martin Beneke)
Our research is in theoretical particle physics. We are interested in high-energy collider phenomenology, perturbative loop calculations, searches for physics beyond the Standard Model and the phenomenology of the Standard Model, the physics of heavy quarks (bottom, top), CP violation, strong interaction physics and some aspects of cosmology/dark matter.
Theoretical Solid-State Physics (Prof. Frank Pollmann)
We are interested in a variety of problems in condensed matter theory. Our main focus lies on the study of phenomena which arise due to quantum mechanical effects in systems of correlated electrons. Areas of research include the study of topological phases of matter, geometrically frustrated systems, dynamics in quantum many-body systems, and the applications of quantum information concepts to condensed matter physics.
Theoretical Physics of the Early Universe (Prof. Björn Garbrecht)
The cosmic evolution depends sensitively on initial conditions, such as the matter-antimatter asymmetry, the Dark Matter abundance and density perturbations, that eventually grow into galaxies. Understanding the initial conditions is one of the key motivations for exploring Physics beyond the Standard Model. Cosmology thus complements laboratory experiments such as the Large Hadron Collider. The particular research interests of our group encompass the origin of the matter-antimatter asymmetry and of density perturbations from inflation.
Theoretical Particle Physics (Prof. Lorenzo Tancredi)

Our main research interest is at the interface between new mathematical methods in quantum field theory and high-energy particle physics phenomenology. We study the mathematical structures which hide behind scattering amplitudes and Feynman diagrams, with the goal of developing new methods to study the dynamics of the Standard Model of particle physics. This will help us, among the others, to understand the details of the spontaneous symmetry breaking mechanism and the properties of the Higgs boson and, possibly, it will pave the way to discover signs of New Physics.
Theoretical Particle Physics at Colliders (Prof. Andreas Weiler)

The aim of our work is to develop plausible theories that address the problems of the Standard Model and to derive signatures, which can be tested at experiments like the Large Hadron Collider at CERN. The central question is the nature of electro-weak symmetry breaking, and the properties of the Higgs particle, which is central to the whole enterprise. The properties of the electroweak symmetry breaking sector remain nebulous, and yet there is no doubt their influence is crucial in many areas of physics such as flavour and CP violation, early Universe cosmology and dark-matter.
Theoretical Particle and Nuclear Physics (Prof. Nora Brambilla)

Effective Quantum Field Theories (EFTs) are the state-of-the-art tools for analyzing physical systems that contain many different energy or momentum scales. Such systems are the rule, rather than the exception, from the "high"-energy domain of Particle Physics to the "low"-energy domain of Nuclear Physics.
Theory of Biological Networks (Prof. Karen Alim)
How does shape and structure emerge when organisms grow? We want to identify the physics that governs the morphing of life. To succeed we combine quantitative observation of life with theoretical models to finally capture the key processes in simple mathematical terms. Life still hides many fundamental processes that once uncovered can revolutionize our designs, engineering or medical treatment.
Theory of Functional Energy Materials (Prof. David Egger)
We conduct research on microscopic theories for functional materials with the goal to find new compounds that will make energy devices, such as solar cells and batteries, more efficient.
Theory of Complex Bio-Systems (Prof. Ulrich Gerland)

In physics, interactions between particles follow laws. In biology, interactions between biomolecules serve a function. We study the physics of biological functions. In particular, we are interested in cases where the implementations of biological functions are constrained by physical principles. Methods from statistical physics help to describe the functioning of complex biomolecular systems on a coarse-grained, but quantitative level.
Topology of Correlated Systems (Prof. Christian Pfleiderer)

Scientific activities covered at our institute include the fundamental properties of magnetic and superconducting materials (bulk compounds and thin films), materials science and a few selected problems in particle physics. The institute has a long tradition in neutron related research, notably the development of state-of-the-art neutron scattering techniques.
Many Particle Phenomena
Research in the theory group led by Prof. Wilhelm Zwerger is focused on quantum and statistical physics in a wide range of areas, from condensed matter physics and nanostructures to ultracold gases and the interface between quantum optics and solid state physics. We are working in collaboration with a number of groups in the Munich area and beyond, in particular with the Max-Planck-Institute for Quantum Optics (MPQ) and within the Nano-Inititative Munich (NIM).
Cellular Biophysics (Prof. Andreas Bausch)
Understanding complex biomaterials on a fundamental physical basis is an integral challenge of future biophysical research. This challenge can be addressed by the concerted application of new experimental tools of soft condensed matter physics to living cells and bio-mimetic model systems. In our group we concentrate on the one hand on developing new physical tools to address the underlying complexity and mechanisms and on the other hand on developing new biomaterials for applications ranging from biomedicine to functional food.